CompletableFuture
2022年5月6日
CompletableFuture
Future和Callable接口
了解CompletableFuture需先了解下Future和Callable接口
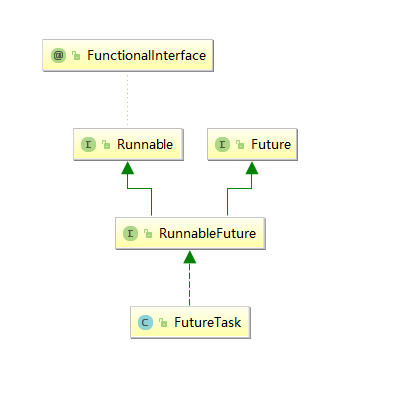
Future
Future接口代表异步计算的结果,通过Future接口提供的方法可以查看异步计算是否执行完成,或者等待执行结果并获取执行结果,同时还可以取消执行。Future接口的定义如下:
public interface Future<V> {
boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning);
boolean isCancelled();
boolean isDone();
V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;
V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
}
cancel():cancel()方法用来取消异步任务的执行。如果异步任务已经完成或者已经被取消,或者由于某些原因不能取消,则会返回false。如果任务还没有被执行,则会返回true并且异步任务不会被执行。如果任务已经开始执行了但是还没有执行完成,若mayInterruptIfRunning为true,则会立即中断执行任务的线程并返回true,若mayInterruptIfRunning为false,则会返回true且不会中断任务执行线程。isCanceled():判断任务是否被取消,如果任务在结束(正常执行结束或者执行异常结束)前被取消则返回true,否则返回false。isDone():判断任务是否已经完成,如果完成则返回true,否则返回false。需要注意的是:任务执行过程中发生异常、任务被取消也属于任务已完成,也会返回true。get():获取任务执行结果,如果任务还没完成则会阻塞等待直到任务执行完成。如果任务被取消则会抛出CancellationException异常,如果任务执行过程发生异常则会抛出ExecutionException异常,如果阻塞等待过程中被中断则会抛出InterruptedException异常。get(long timeout,Timeunit unit):带超时时间的get()版本,如果阻塞等待过程中超时则会抛出TimeoutException异常。
Callable
Callable是个泛型接口,泛型V就是要call()方法返回的类型。对比Runnable接口,Runnable不会返回数据也不能抛出异常。
public interface Callable<V> {
/**
* Computes a result, or throws an exception if unable to do so.
*
* @return computed result
* @throws Exception if unable to compute a result
*/
V call() throws Exception;
}
示例
@Test
public void testFutureTask() throws Exception{
FutureTask<Integer> futureTask = new FutureTask<Integer>(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"--futureTask--com");
return 123;
});
new Thread(futureTask).start();
System.out.println(futureTask.get());//这里的get方法会阻塞
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"---main");
}
CompletableFuture
简单介绍
- 在Java8中,CompletableFuture提供了非常强大的Future的扩展功能,可以帮助我们简化异步编程的复杂性,并且提供了函数式编程的能力,可以通过回调的方式处理计算结果,也提供了转换和组合CompletableFuture的方法。
- 它可能代表一个明确完成的Future,也有可能代表一个完成阶段(CompletionStage),它支持在计算完成以后触发一些函数或执行某些动作。
- 同时实现了
Future和CompletionStage接口。
相比Future的有点
- 异步任务结束时,会自动回调某个对象的方法;
- 异步任务出错时,会自动回调某个对象的方法;
- 主线程设置好回调后,不再关心异步任务的执行,异步任务之间可以顺序执行
简单案例
runAsync 无 返回值
//runAsync 无返回值
@Test
public void test_runAsync()throws Exception{
CompletableFuture completableFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"this is completableFuture");
try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
});
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"this is main");
}
supplyAsync 有 返回值
//supplyAsync 有返回值
@Test
public void test_supplyAsync()throws Exception{
CompletableFuture completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"this is completableFuture");
try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
return "supplyAsync";
});
System.out.println(completableFuture.get());
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"this is main");
}
结合whenComplete有返回值,但是不会阻塞
//有返回值,但是不会阻塞
@Test
public void test_return()throws Exception{
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "-----come in");
int result = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(10);
//暂停几秒钟线程
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
System.out.println("-----计算结束耗时1秒钟,result: "+result);
if(result > 6)
{
int age = 10/0;
}
return result;
}).whenComplete((v,e) ->{//v是返回值,e是出现异常
if(e == null)
{
System.out.println("-----result: "+v);//这里直接获取返回值
}
}).exceptionally(e -> {//如果有异常
System.out.println("-----exception: "+e.getCause()+"\t"+e.getMessage());
return -44;//如果有异常返回-44
});
// System.out.println(completableFuture.get());//这种写法相当于 Future的写法,还会阻塞主线程
// System.out.println(completableFuture.join());//join 和 get 都会阻塞,但是join不会报异常
System.out.println("this is main");
//主线程不要立刻结束,否则CompletableFuture默认使用的线程池会立刻关闭:暂停3秒钟线程
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
}
CompletableFuture常用操作
获得结果和触发计算
获取结果
public T get()
public T get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)//过时不候
public T getNow(T valueIfAbsent)//没有计算完成,给我一个替代结果。计算完,返回正确结果;没算完,返回设定的valueIfAbsent值
主动触发计数
public boolean complete(T value) //是否打断get方法立即返回括号值
@Test
public void test_supplyAsc()throws Exception{
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
return 533;
});
//注释掉暂停线程,get还没有算完只能返回complete方法设置的444;暂停2秒钟线程,异步线程能够计算完成返回get
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
//当调用CompletableFuture.get()被阻塞的时候,complete方法就是结束阻塞并get()获取设置的complete里面的值.
System.out.println(completableFuture.complete(444)+"\t"+completableFuture.get());
}
对计算结果进行处理
thenApply
计算结果存在依赖关系,这两个线程串行化
由于存在依赖关系(当前步错,不走下一步),当前步骤有异常的话就叫停。
@Test
public void test() {
//当一个线程依赖另一个线程时用 thenApply 方法来把这两个线程串行化,
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//暂停几秒钟线程
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
System.out.println("111");
return 1024;
}).thenApply(f -> {
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
System.out.println("222");
return f + 1;
}).thenApply(f -> {
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
//int age = 10/0; // 异常情况:那步出错就停在那步。
System.out.println("333");
return f + 1;
}).whenCompleteAsync((v,e) -> {
System.out.println("*****v: "+v);
}).exceptionally(e -> {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
});
System.out.println("-----主线程结束,END");
// 主线程不要立刻结束,否则CompletableFuture默认使用的线程池会立刻关闭:
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
}
handle
有异常也可以往下一步走,根据带的异常参数可以进一步处理
@Test
public void test1() {
//当一个线程依赖另一个线程时用 handle 方法来把这两个线程串行化,
// 异常情况:有异常也可以往下一步走,根据带的异常参数可以进一步处理
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//暂停几秒钟线程
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
System.out.println("111");
return 1024;
}).handle((f,e) -> {
int age = 10/0;
System.out.println("222");
return f + 1;
}).handle((f,e) -> {
System.out.println("333");
return f + 1;
}).whenCompleteAsync((v,e) -> {
System.out.println("*****v: "+v);
}).exceptionally(e -> {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
});
System.out.println("-----主线程结束,END");
// 主线程不要立刻结束,否则CompletableFuture默认使用的线程池会立刻关闭:
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
}
对计算结果进行消费
thenAccept
接收任务的处理结果,并消费处理,无返回结果
@Test
public void test_thenAccept(){
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
return 1;
}).thenApply(f -> {
return f + 2;
}).thenApply(f -> {
return f + 3;
}).thenApply(f -> {
return f + 4;
}).thenAccept(r -> System.out.println(r));
}
thenRun
任务 A 执行完执行 B,并且 B 不需要 A 的结果
thenAccept
任务 A 执行完执行 B,B 需要 A 的结果,但是任务 B 无返回值
thenApply
任务 A 执行完执行 B,B 需要 A 的结果,同时任务 B 有返回值
对计算速度进行选用
applyToEither
谁快用谁
@Test
public void test_applyToEither()throws Exception{
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "---come in ");
//暂停几秒钟线程
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
return 10;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "---come in ");
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
return 20;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> thenCombineResult = completableFuture1.applyToEither(completableFuture2,f -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "---come in ");
return f + 1;
});
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + thenCombineResult.get());
}
对计算结果进行合并
thenCombine
两个CompletionStage任务都完成后,最终能把两个任务的结果一起交给thenCombine 来处理
先完成的先等着,等待其它分支任务
- 标准版,好理解
@Test
public void test_thenCombine()throws Exception{
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "---come in ");
return 10;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "---come in ");
return 20;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> thenCombineResult = completableFuture1.thenCombine(completableFuture2, (x, y) -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "---come in ");
return x + y;
});
System.out.println(thenCombineResult.get());
}
- 流式编程版本
@Test//流式编程版本
public void test_thenCombineB()throws Exception{
CompletableFuture<Integer> thenCombineResult = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "---come in 1");
return 10;
}).thenCombine(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "---come in 2");
return 20;
}), (x,y) -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "---come in 3");
return x + y;
}).thenCombine(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "---come in 4");
return 30;
}),(a,b) -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "---come in 5");
return a + b;
});
System.out.println("-----主线程结束,END");
System.out.println(thenCombineResult.get());
// 主线程不要立刻结束,否则CompletableFuture默认使用的线程池会立刻关闭:
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
}
